Abstract
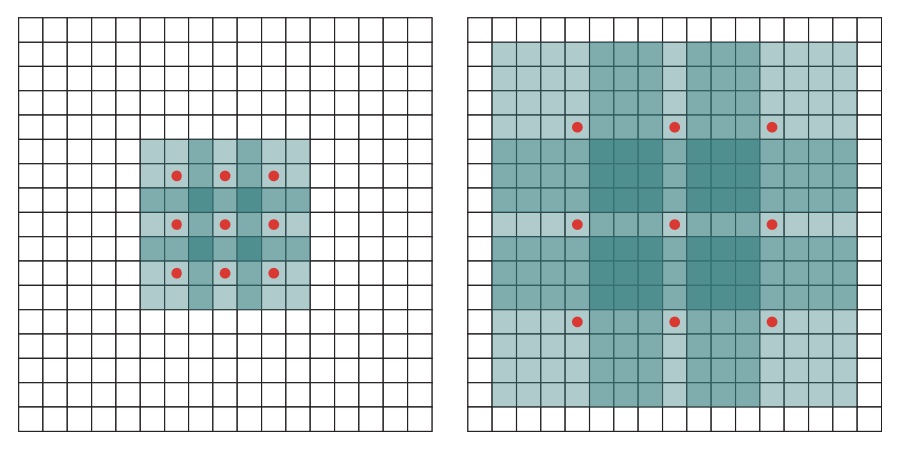
State-of-the-art models for semantic segmentation are based on adaptations of convolutional networks that had originally been designed for image classification. However, dense prediction and image classification are structurally different. In this work, we develop a new convolutional network module that is specifically designed for dense prediction. The presented module uses dilated convolutions to systematically aggregate multi-scale contextual information without losing resolution. The architecture is based on the fact that dilated convolutions support exponential expansion of the receptive field without loss of resolution or coverage. We show that the presented context module increases the accuracy of state-of-the-art semantic segmentation systems. In addition, we examine the adaptation of image classification networks to dense prediction and show that simplifying the adapted network can increase accuracy.
Poster
 Click here to open high-res pdf poster.
Click here to open high-res pdf poster.
Paper
Code
Since the publication of this paper, dilated convolution has been supported by all deep learning frameworks. Here are some popular examples.
Citation
@inproceedings{yu2015multi,
title = {Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions},
author = {Yu, Fisher and Koltun, Vladlen},
booktitle = {International Conference on Learning Representations},
year = {2016}
}