Abstract
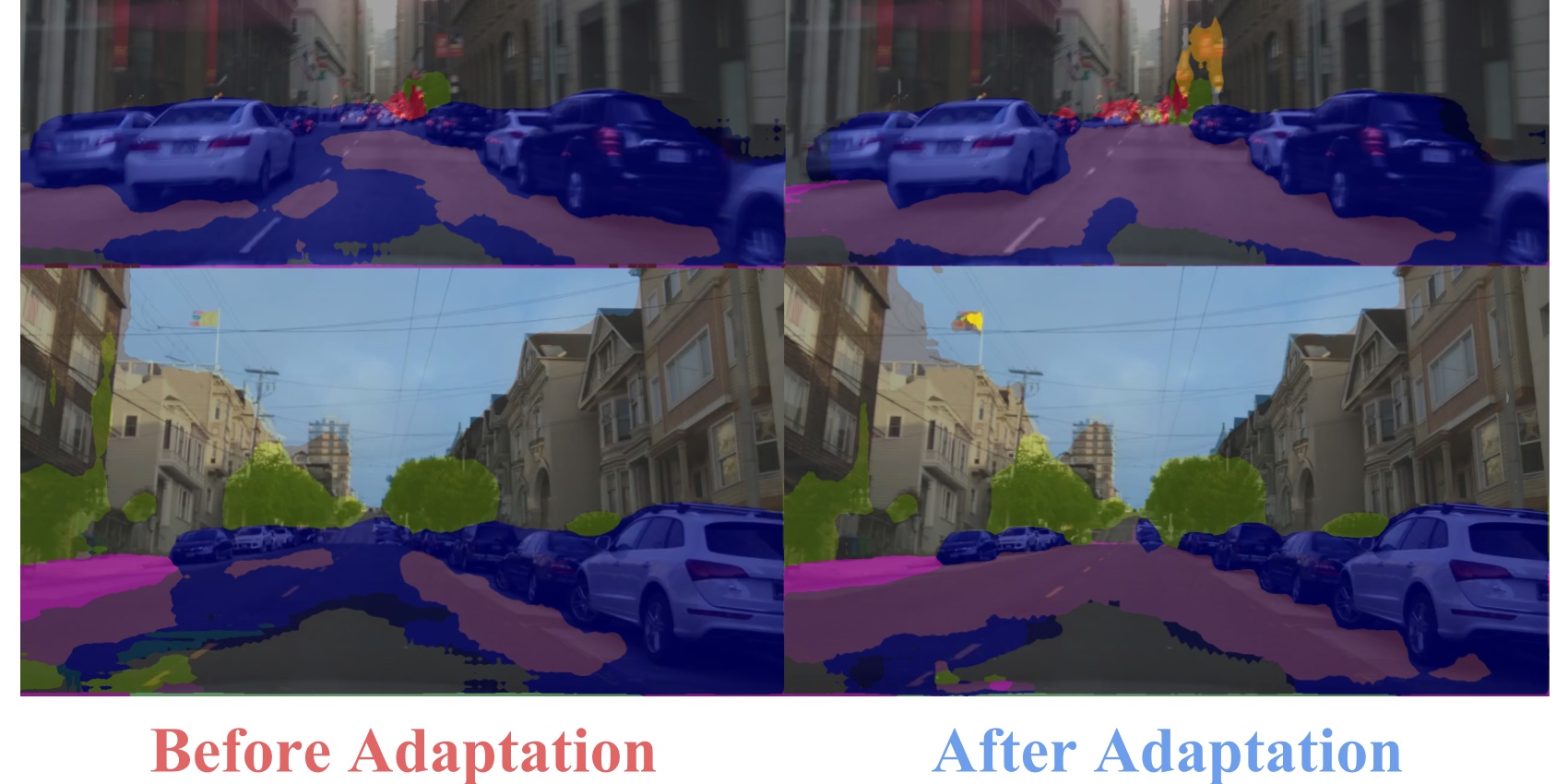
Fully convolutional models for dense prediction have proven successful for a wide range of visual tasks. Such models perform well in a supervised setting, but performance can be surprisingly poor under domain shifts that appear mild to a human observer. For example, training on one city and testing on another in a different geographic region and/or weather condition may result in significantly degraded performance due to pixel-level distribution shift. In this paper, we introduce the first domain adaptive semantic segmentation method, proposing an unsupervised adversarial approach to pixel prediction problems. Our method consists of both global and category specific adaptation techniques. Global domain alignment is performed using a novel semantic segmentation network with fully convolutional domain adversarial learning. This initially adapted space then enables category specific adaptation through a generalization of constrained weak learning, with explicit transfer of the spatial layout from the source to the target domains. Our approach outperforms baselines across different settings on multiple large-scale datasets, including adapting across various real city environments, different synthetic sub-domains, from simulated to real environments, and on a novel large-scale dash-cam dataset.
Paper
 | Judy Hoffman, Dequan Wang, Fisher Yu, Trevor Darrell FCNs in the Wild: Pixel-level Adversarial and Constraint-based Adaptation arXiv 2016 |
Citation
@misc{hoffman2016fcns,
title={FCNs in the Wild: Pixel-level Adversarial and Constraint-based Adaptation},
author={Judy Hoffman and Dequan Wang and Fisher Yu and Trevor Darrell},
year={2016},
eprint={1612.02649},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CV}
}